- START

Updated by Dr Hew Torrance, July 2013.
Introduction
This module deals with the basis of warfarin therapy.
Anticoagulation module 2 contains clinical anticoagulation scenarios.
The delayed and unpredictable consequences of warfarin therapy in individuals is explained.
Why is warfarin therapy of special importance? Approximately half a million people in Britain take warfarin. Between 1963 and 2008 there were 297 deaths in the UK caused by doctors' warfarin prescribing. 208 were due to haemorrhage¹. It is the drug that is the subject of the greatest number of legal actions in the NHS. Good prescribing and follow-up reduces these risks.
References
1. MHRA public assessment report. Warfarin: changes to product safety information. December 2009. Available at www.mhra.gov.uk (accessed July 2013).
Select the most accurate option
- HAEMOSTASIS
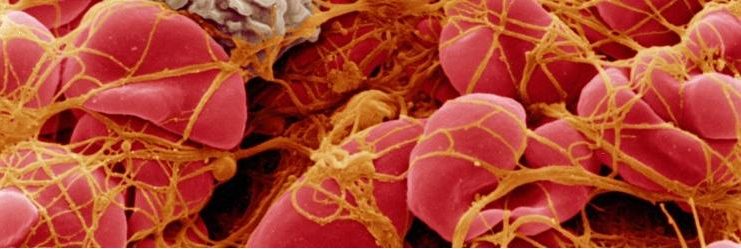
Question 1. What exactly is depicted in red and yellow on the electron micrograph?
As a result of activation of the clotting cascade in the plasma of the blood FIBRIN (Depicted in yellow on the image) has been produced and made into a mesh plug with platelets that is arresting the bleeding of the red blood cells (Depicted in red).
i.e. This is a blood clot
Coumarin anti-coagulants (Warfarin) reduce the effective production of various parts of the clotting cascade. These "parts" are proteins called coagulation factors.
The result is fewer fully functional clotting factors in the circulation. The consequence of this being less easily initiated and slower, impaired coagulation.
- OVERVIEW DIAGRAM
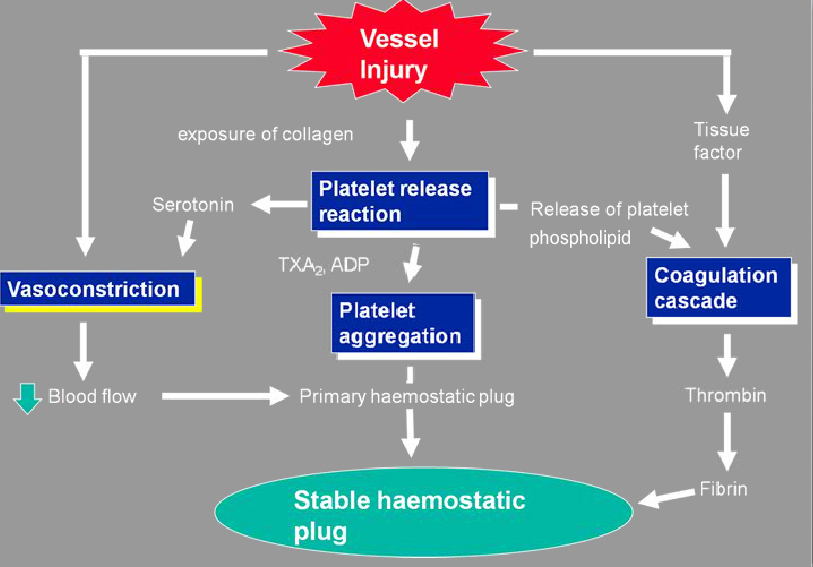
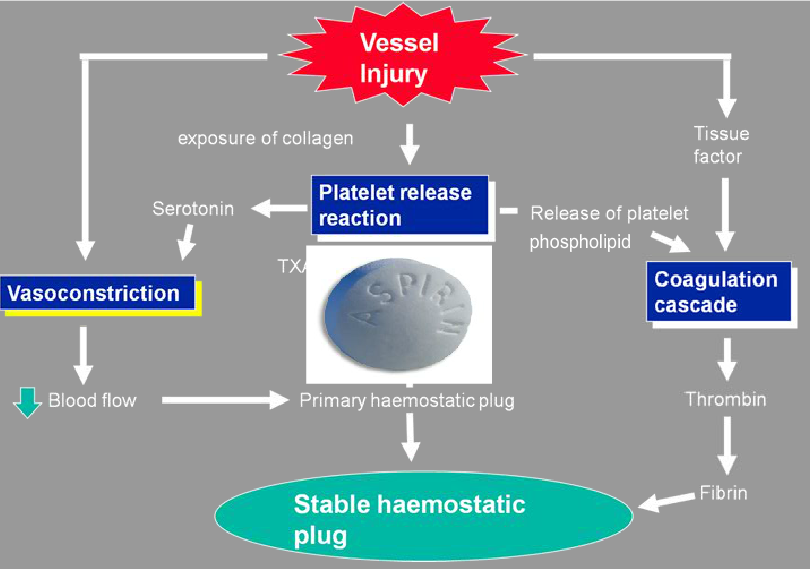
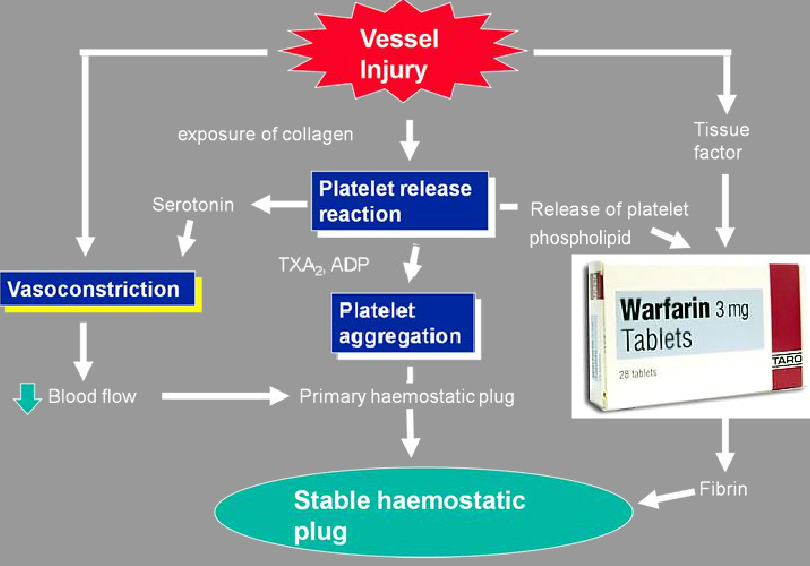
- TIME TO EFFECT
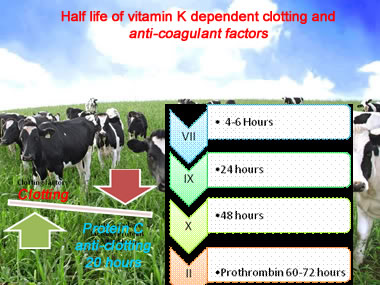
Here are linked concepts: How does warfarin work? = How are clotting factors made? = What is vitamin K essential for?
Vitamin K is metabolically essential for factor II, VII, IX & X as well as anti-coagulant protein C & S production. Vitamin K is recycled in a (oxidation/reduction) reaction that completes structure of the clotting factors by adding a carboxyl (carbon & oxygen) group.
Warfarin inhibits the recycling of vitamin K, and thus structurally incomplete factors are produced. New (more ) vitamin K is required to overcome this deficit.
Josie Smith, 75, with diabetes and previous ischaemic stroke is started on daily wafarin as she has atrial fibrillation.
After 24 hours what effect will the warfarin have?
- MONITORING THERAPY
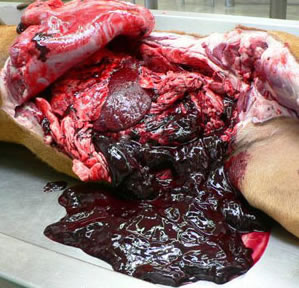
The need for monitoring. (Warfarin overdose in a dog at post-mortem)
He did not and could not know what warfarin dose to take, or when he needed his blood tested, and he could not understand the reasons.
It is our job that we give warfarin to patients who understand and are able and willing to deal with this treatment.
The resulting level of anti-coagulation is very variable between individuals.
Warfarin put in & absorbed - minus Vitamin K put in & produced. Then account for the individual's hepatic function plus their speed of warfarin metabolism = Production of functional clotting factors including (pro)thrombin.
The problem is that the only known "certainty" Is the warfarin dose. Everything else is variable.
In practice how do we determine how much anti-coagulation will/has resulted from a given dose of Warfarin?
What makes warfarin therapy possible is our ability to measure the resulting level of anticoagulation in the form of the prothrombin time. i.e. a blood test result.
This is then expressed as an International Normalised Ratio (INR) test results in universal ease of use. An INR number of 1.0 is expected for a healthy person not taking any anticoagulant treatment.
Doses are varied to match a certain INR target figure, not the level of warfarin in the body etc.
If the dose is changed every day, then it is almost impossible to know what effect one dose alteration has.
(Why? see next page)
How can anticoagulation by warfarin be instantly reversed?
- DOSING
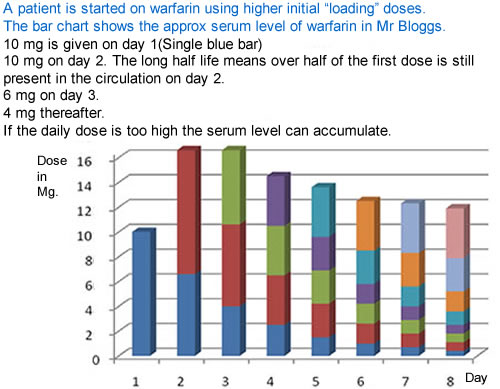
Is there a standard dose? There is no fixed dose. Many patients need 3-9mg daily.
How much difference does one warfarin dose make?
The effective circulating level of warfarin after the loading doses is dominated by the sum of previous doses given, as the half life of warfarin is generally 36-42 hours.
Add that to the 60-72 hour half-life of prothrombin and it is possible to appreciate that the anti-coagulant effect takes a while to increase or decrease.
It is like sailing an oil tanker; Inputs are not followed by rapid responses.
Is warfarin well absorbed? Yes it is quickly and effectively absorbed when taken by mouth.
- METABOLISM

Yes, including enzymes such as CYP450 2C9, and many other P450 isoenzymes.
In practice if another medication is started that "competes" for metabolism via the same pathways warfarin levels could build up causing over-anti-coagulation.
Can the CYP system be "speeded up" or "slowed down"?
Yes, the system can be induced (rifampicin, St John's wort, etc) or inhibited ("azole" antifungals, macrolide antibiotics etc) by any number of drugs and also food stuffs.

The dose and the INR are the only known quantities...
Is the rate of warfarin metabolism in healthy individuals of the same age and size similar?
No, because it depends on their livers' ability to break down warfarin. Some people have a set of genes (i.e. genetic polymorphism) giving them more capable metabolic pathways than others. It also depends on how much spare capacity there is in these pathways.
Is this the Cytochrome P450 enzyme family?
How can you most reliably check if a drug interacts with warfarin or causes P450 induction/inhibition ?
Look in appendix 1 of the BNF
- MINI CASE SCENARIOs
A patient on warfarin for recurrent deep venous thrombosis sees an offer for cranberry juice at the supermarket and buys four packs which she consumes over a week. She then attends for her routine monitoring blood test where the prothrombin time is measured. Later that day she recieves a call from the clinic.
1. Look up the most likely effect this has on the INR. 2. Explain why. 3. What would you do?
1. The prothrombin time and INR is likely to increase.
2. The metabolism of warfarin by the liver through CYP 450 enzyme system is reduced.
3. Advise the patient either to avoid cranberry juice or drink a more moderate amount regularly.
Lets say the INR comes back at 5.9 If there are no signs of bleeding then doses are omitted till the INR is below 5.0 If the INR is over 8.0 doses are omitted and vitamin K is given.
An elderly patient who lives on her own is six weeks into three months of warfarin treatment for a first pulmonary embolism. Her INR and dose has been very stable. She goes to stay with her daughter, a school teacher, over the summer holidays, and enjoys big wholesome meals with the family.
Briefly explain what changes may occur to her anti-coagulation & why.
Her total food consumption may increase. Wholesome meals in summer time could imply an increased intake of fresh vegetables. Overall her vitamin k intake may rise significantly, increasing the number of complete clotting factors in her circulation, which will decrease her prothrombin time & INR, increasing her dose requirement.
Anticoagulation module 2 contains interactive short cases relevant to clinical practice covering:
Indications for anti-coagulation.
Using risk assessment tools such as CHADS2VASc & HASBLED
Contraindications to anti-coagulation.
Alternative anti-coagulants to vitamin K antagonists. (warfarin)